Page 9 - Atlas_2019_rus
P. 9
Motor vehicle infrastructure
Motorways link up the region, connecting its vast territory and providing access to other countries and neighbouring
regions, while also facilitating the carriage of cargoes and passengers. These motor transport links provide secure,
reliable connections to other transportation terminals for sea, river, rail, and air transport. The roads also connect
to border checkpoints, centres of production and all consumption locations and local communities.
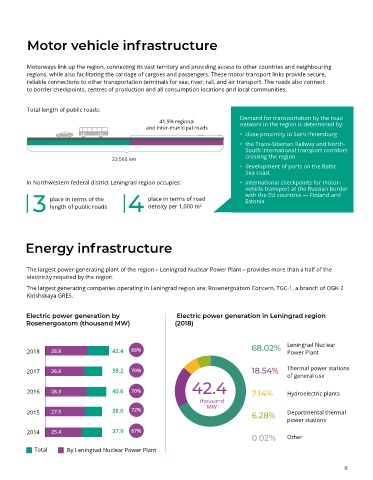
Total length of public roads:
Demand for transportation by the road
41.9% regional network in the region is determined by:
and inter-municipal roads
• close proximity to Saint Petersburg
• the Trans-Siberian Railway and North-
South international transport corridors
22,560 km crossing the region
• development of ports on the Baltic
Sea coast
In Northwestern federal district Leningrad region occupies: • international checkpoints for motor-
vehicle transport at the Russian border
3 place in terms of the 4 place in terms of road with the EU countries — Finland and
Estonia
length of public roads
density per 1,000 m
2
Energy infrastructure
The largest power-generating plant of the region – Leningrad Nuclear Power Plant – provides more than a half of the
electricity required by the region.
The largest generating companies operating in Leningrad region are: Rosenergoatom Concern, TGC-1, a branch of OGK-2
Kirishskaya GRES.
Electric power generation by Electric power generation in Leningrad region
Rosenergoatom (thousand MW) (2018)
2018 28.8 42.4 68% 68.02% Leningrad Nuclear
Power Plant
2017 26.8 38.2 70% 18.54% Thermal power stations
of general use
42.4
2016 28.3 40.6 70% 7.14% Hydroelectric plants
thousand
MW
2015 27.5 38.0 72% 6.28% Departmental thermal
power stations
2014 25.4 37.9 67%
0.02% Other
Total By Leningrad Nuclear Power Plant
9